Services
Cell Culture Systems
CELL CULTURE SYSTEMS – HUMAN AND RODENT
- Primary human and rodent cell/tissue culture from multiple organ systems
- Long-term normal and transformed cell line culture
- Dose-response testing in cells to define drug activity or toxicity
- Generation of cell culture supernatants for growth factors, proteins, and matrix components
- Development of client-specific cell culture models for drug screening
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS:
- Screening of compounds for activity or toxicity
- Defining human primary cell or cell line responses
- Supplementing of internal cell culture resources
- Mechanistic determinations of drug efficacy or toxicity
- Advanced cell culture approaches to mimic in vivo conditions
- Comparative testing of preclinical and clinical drug responses
- Cost-effective development new cell-based models
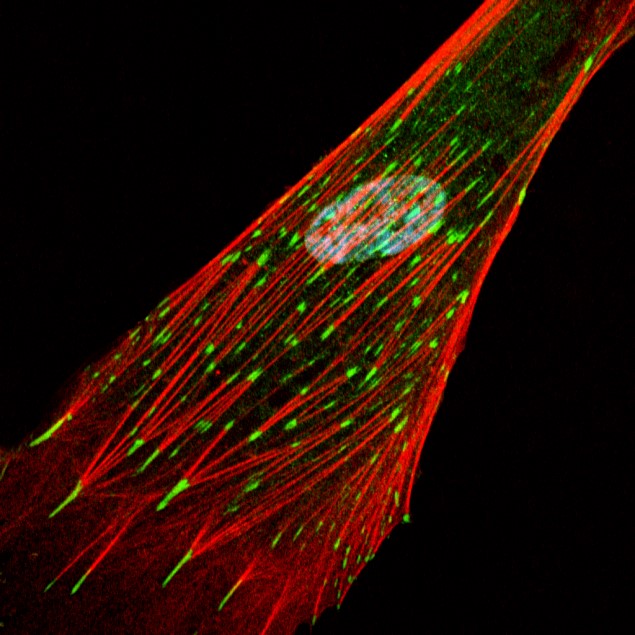
Human Skin Organ Culture
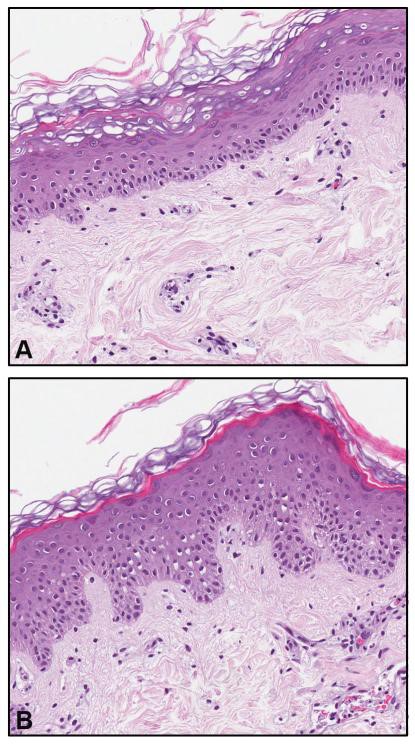
– Multiple replicate cultures from each skin donor
– Viability and homeostasis maintained for weeks in culture
– Healthy skin, aged skin, photodamaged skin, psoriatic, diabetic skin etc.
– Can be used in conjunction with primary culture keratinocytes and fibroblasts from same donors
– Useful for early stage (pre-clinical) assessment of:
- Skin toxicity, corrosivity, contact irritation, contact sensitization
- Epidermal hyperplasia and skin thickening; Normal and abnormal differentiation and barrier function
- Skin atrophy / skin aging / prevention
- Dermal effects: Collagen, proteoglycan and glycoprotein production and degradation, MMPs, MMP activation and inhibition, other proteinases
- Fibroproliferative and fibrotic changes
- UV-skin damage
- Effects on hair follicles, sebaceous glands etc.
- Mast cell biology, vascular biology, melanocyte biology
- Skin immunology
– Organ-cultured skin useful for assessing cytokines, growth factors and other molecules of interest; Used for gene array and proteomic analysis; signaling pathway assessment
– Amenable to structural analysis: histology / cytology, immunohistology / immunofluorescence; and ultrastructure (TEM, SEM)
– Scientists at JV Biolabs have over 100 publications in use of this technology
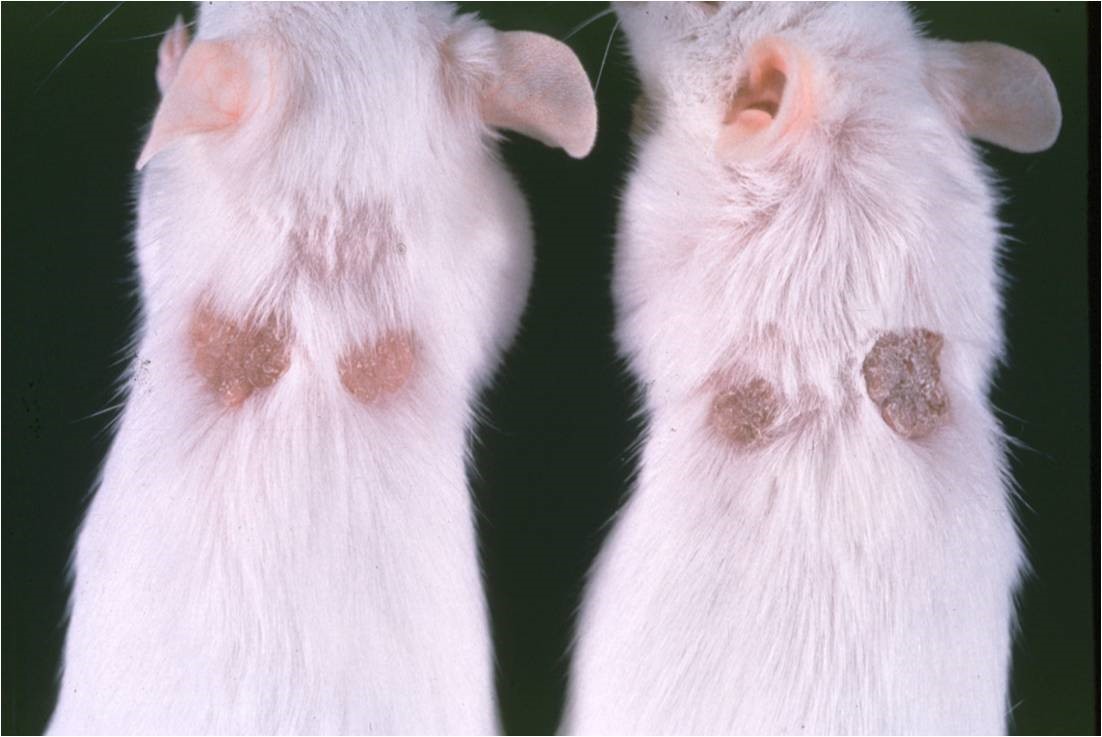
human psoriatic skin – scid mouse transplant model
- The human psoriatic skin – scid mouse transplant model is the industry accepted model for preclinical assessment of potential anti-psoriatic agents.
- JV BIOLABS has over 10 years of experience with this model.
- Can assess clinical changes, histology features and immunohistology. Changes in growth factor / cytokine production with treatment.
- Topical, systemic and oral dosing is possible.
- Transplantation model can be used alone for demonstration of therapeutic efficacy.
- Transplantation model can be used in conjunction with human skin organ culture and keratinocyte culture to assess mechanisms of action.
Rhinomouse Model
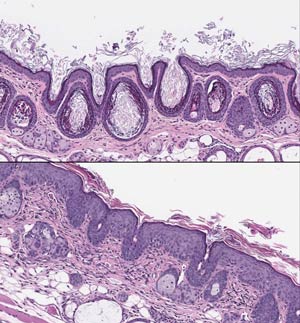
THE RHINOMOUSE MODEL IS THE INDUSTRY ACCEPTED MODEL FOR PRECLINICAL ASSESSMENT OF RETINOIDS FOR ANTI-ACNE ACTIVITY
- JV Biolabs has over 15 years of experience with this model
- Assess efficacy (anti-keratinization), inflammation, skin irritation, systemic toxicity in same
- experiment
- Topical, systemic and oral dosing possible
- Native molecules and formulated products can be employed
- Can be used alone for demonstration of therapeutic efficacy
- Can be used in conjunction with human skin organ culture and keratinocyte culture to assess
- mechanisms of action
- Non-retinoids compounds can also be evaluated in the rhinomouse model
Vascular Biology and Endothelial Cell Models
SYSTEMS FOR ENDOTHELIAL BIOLOGY
- Acute and chronic vascular injury models
- Human primary endothelial cells and established cell lines
- Healthy volunteer, psoriatic, Rosacea, cancer, and fibrotic systems
- Cytokine, integrin, and cellsurface marker characterization of vessels or individual cells
- Rodent, bovine and pocine endothelial cells and tissues
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Direct and indirect drug-mediated injury
- Localized injection site responses
- Drug compatibility and irritation assessment
- Mechanistic determinations of vascular changes
- Apoptotic and anti-apoptotic mechanisms
- Assessment of angiogenic and anti-angiogenic activity
- Drug-induced vascular toxicity
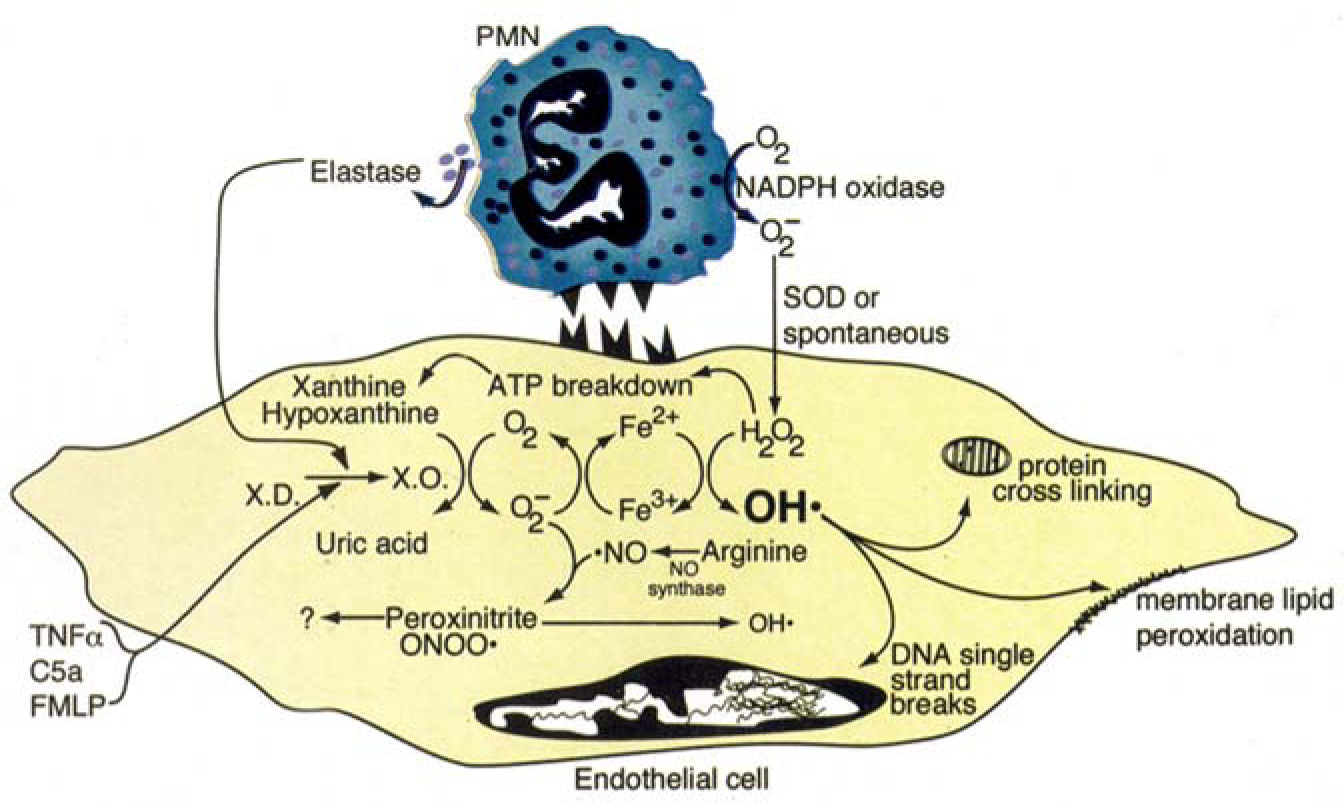
Kidney Injury Models
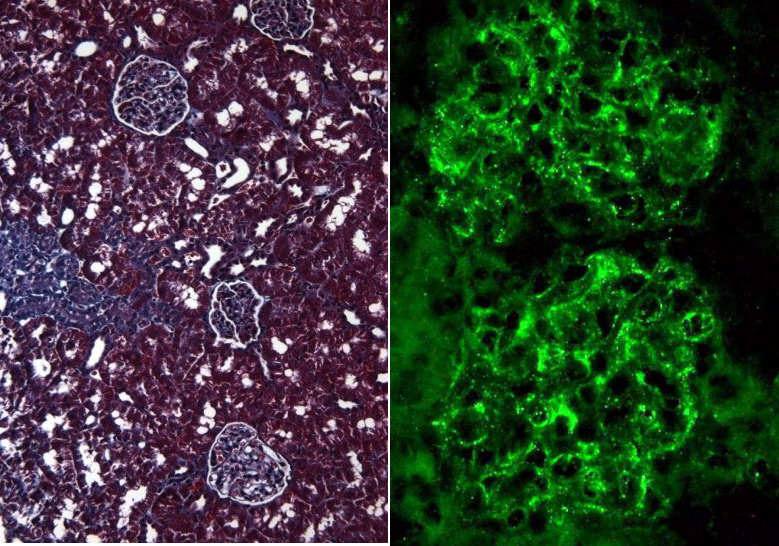
SYSTEMS FOR DETECTING RENAL INJURY AND FUNCTION
- In vivo models of drug-induced nephrotoxicity, diabetes, vasculitis, and glomerulonephritis
- In vivo models of vasculitis and imflammatory injury
- In vivo characterization of glomerular microangiopathic injury
- Human and rodent podocyte culture – primary and cloned cells
- Mesangial and tubular cell culture
- ELISA and standard clinical pathology monitoring of renal biomarkers
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Detection of drug-induced changes on kidney and kidney function
- Screening of drug candidates for kidney toxicity
- Direct and indirect drug-mediated injury characterization
- Mechanistic determinations of pharmacologic activity
- Specific characterization of kidney injury pathways
- Therapeutic potential of new therapies – small molecule and biologic
Human, Cynomologus Monkey, and Rodent Mast Cell Assays
IN VITRO CHALLENGE OF ISOLATED MAST CELLS
- Rat Peritoneal Mast Cells
- Human Mast Cell Line
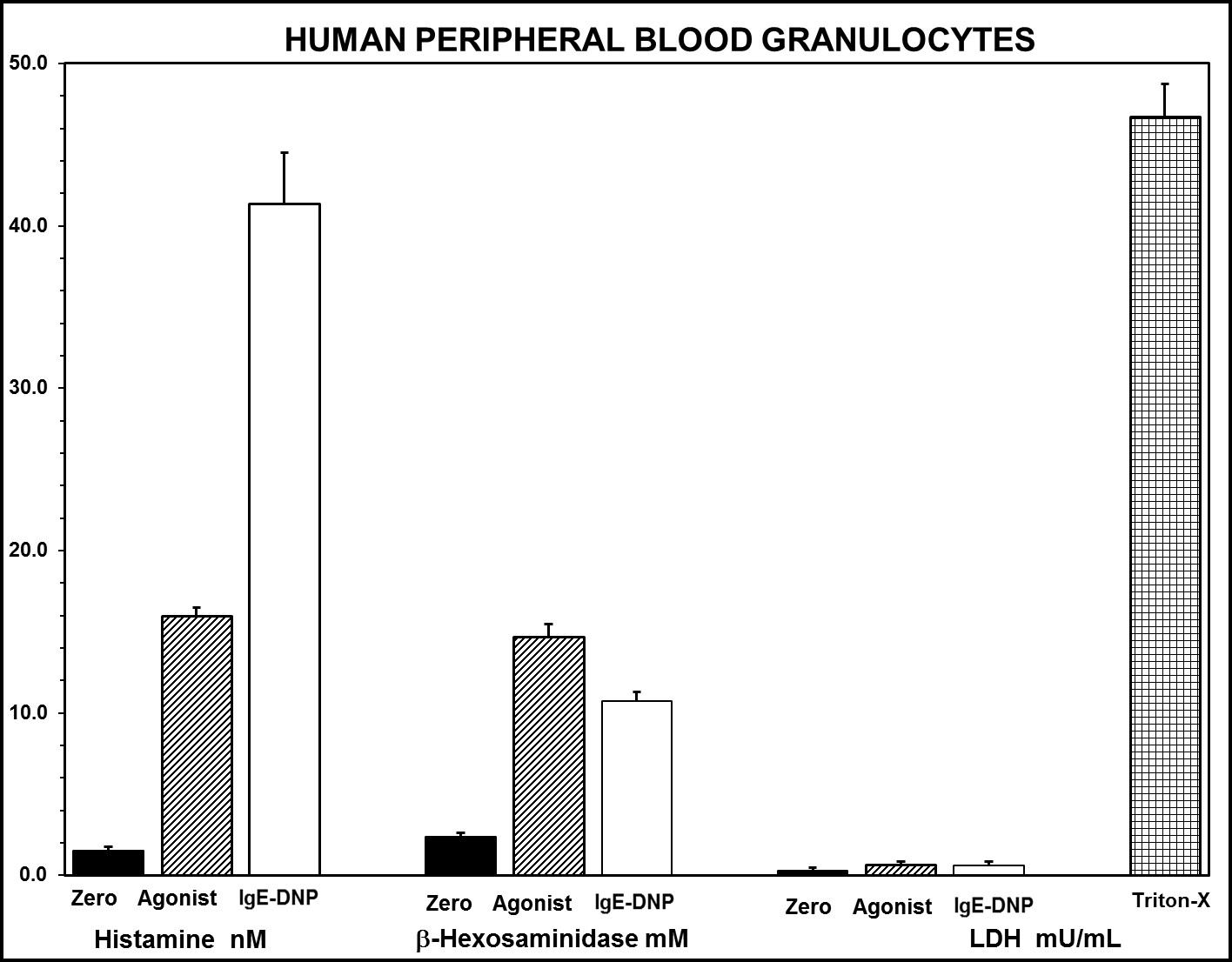
- Human Peripheral Blood Granulocytes
- Cynomolgous Monkey Peripheral Blood Granulocytes
DETERMINATIONS OF MAST CELL DEGRANULATION
HUMAN & CYNOMOLOGUS MONKEYS
- Histamine
- Tryptase
- Beta-Hexosaminidase
- Toxicity as measured by LDH
RAT MAST CELLS
- Histamine
- Tryptase
- Chymase
- Toxicity as measured by LDH
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Screening of compounds for hypersensitivity potential
- Screening of compounds for mast cell activation
- Suppression of mast cell activation
Human And Animal Models For Mast Cell Biology
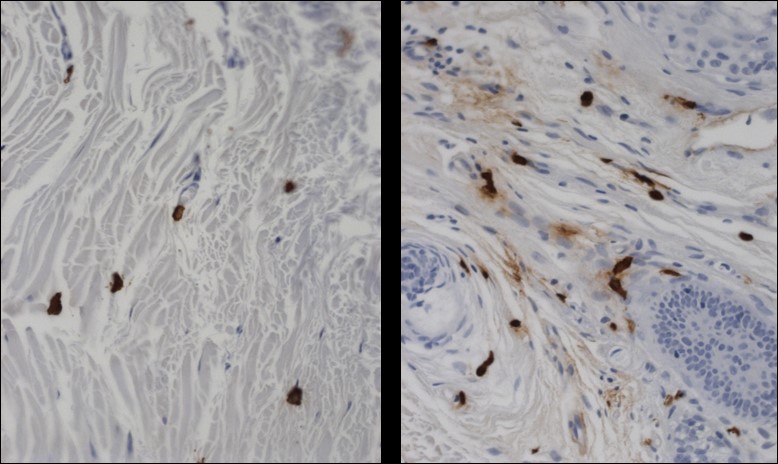
HUMAN AND RODENT MAST CELL SYSTEMS
- Human skin organ culture to assess mast cell numbers and degranulation
- In vitro challenge of rat peritoneal mast cells for histamine and/or IL-17 release
- Measurement of histamine, chymase, tryptase, and IL-17 release
- Histology and cytology using immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure methods
- Development of client-specific applications for drug screening
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Screening of compounds for immediate hypersensitivity potential
- Supplementing of internal testing resources
- Mechanistic determinations of drug efficacy or toxicity
- Suppression of mast cell activation
- Comparative testing of preclinical and clinical drug responses
Proteomic Micro-Arrays
SYSTEMS FOR PLASMA, SERUM, AND CELL CULTURE SUPERNATANTS
Rapid and specific measurement of:
- Cytokines and chemokines
- Inflammatory proteins
- Growth and angiogenesis factors
- Protease and protease inhibitors
- Cell adhesion molecules
- Heat shock proteins
- Complement proteins
- Anti-coagulant factors
- >100 Human proteins and >45 rat proteins detected on the standard antibody array with low pg detections
- Custom microarray development
- High sample throughput with semiquantitation evaluation of multiple individual proteins
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Analysis of clinical and preclinical samples for biomarker development
- Detection of auto-antibodies
- Direct and indirect drug-mediated injury characterization
- Mechanistic determinations of pharmacologic and toxicologic activity
- Sample screening to determine which proteins to target in renal disease,
- inflammatory reactions, auto-immunity, and transplantation

Research ELISA Development And Conduct
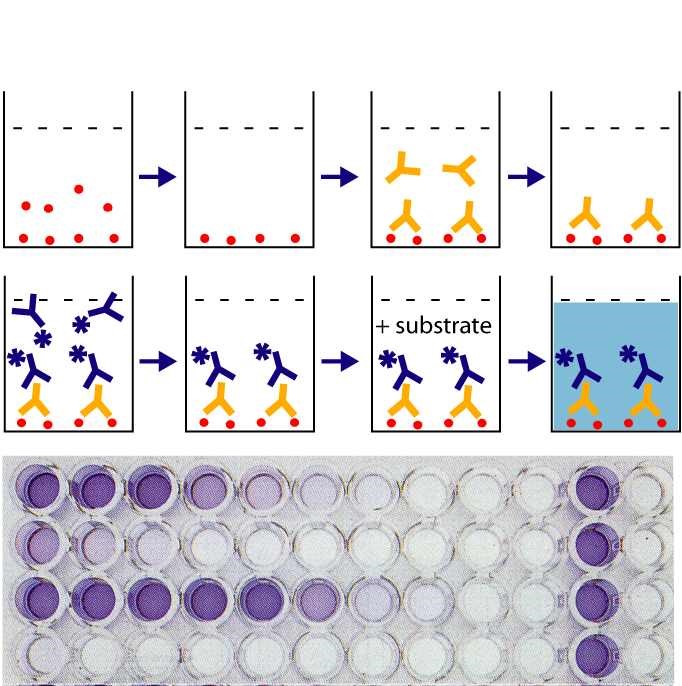
ELISA OFFERINGS
- Accurate and reproducible performance of commercial or client ELISA assays
- Development of new research ELISA methods to client’s performance specifications
- Analysis of human, animal, and cell culture samples
- Extensive menu of available cytokine, protease, peptide, and growth factor assays
- Generation of positive control reagents and reference materials
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Characterization of drug-induced effects from in vitro and in vivo models
- Cost-effective assay development for early-stage applications
- Mechanistic study support
- Supplementing of internal resources for sensitive ELISA methods
- Exploratory investigations of clinical specimens
- Screening immunogenicity determinations
- Third-part validation of test results
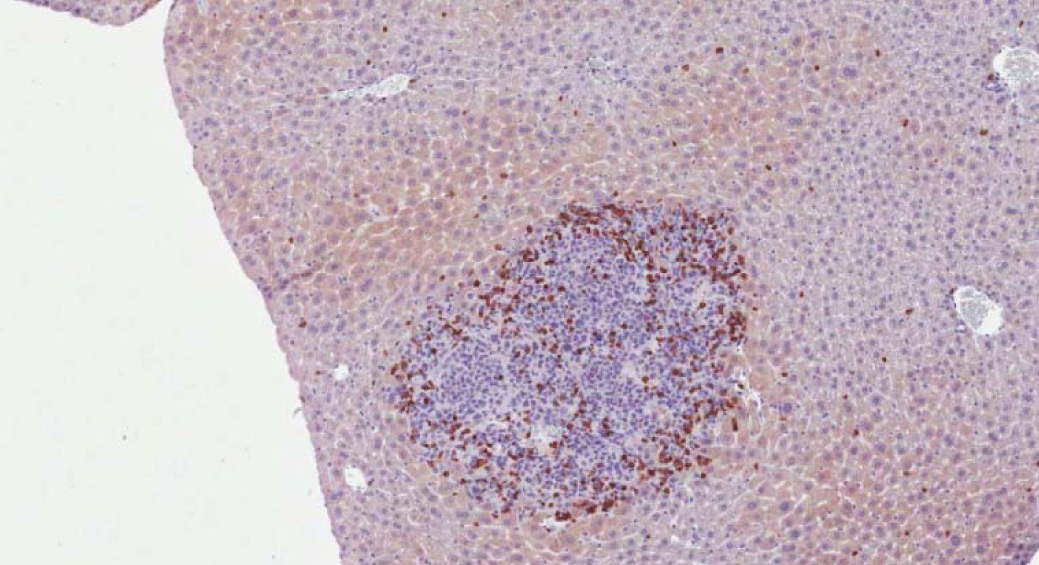
Tumor Immunology
FULL RANGE OF MODELS FOR STUDY OF TUMOR IMMUNOLOGY
- Human tumors in xenograft models
- Rodent tumors in syngeneic host
- Carcinogenesis / anti-carcinogenesis models
- 2D and 3D cell culture
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Preclinical assessment in support of Mab and vaccine development programs
- Detection and quantification of target molecules on tumor cells and normal counterparts by confocal immunofluoresce microscopy, flow cytometry, immunohistology, ELISA and western blotting
- Assessment of efficacy with monoclonal antibodies, peptides and immune modulators in cell culture models, in syngeneic rodent models and in human xenograft models
- Studies to assess mechanisms of action
- Target molecule modulati
Tumor Biology
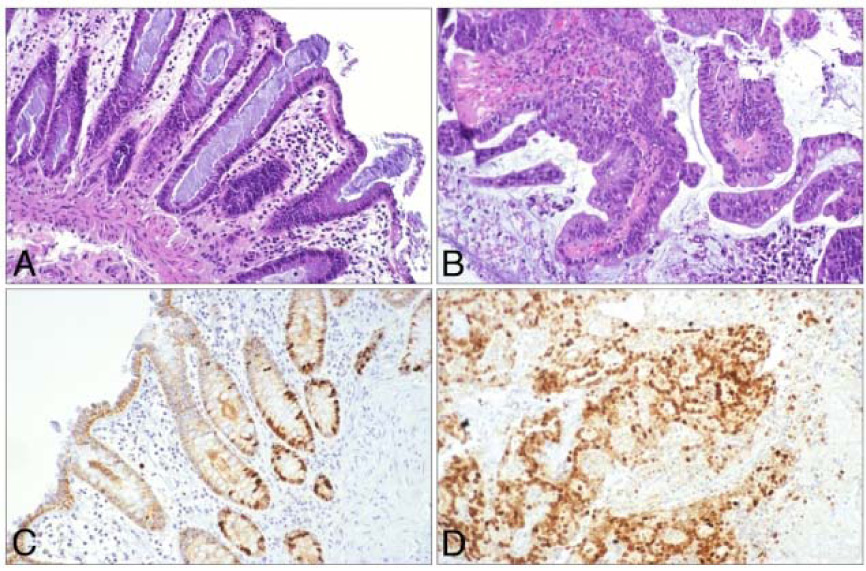
FULL RANGE OF MODEL SYSTEMS OR STUDY OF TUMOR CELL BIOLOGY
- Human tissue – normal, premalignant and malignant in culture
- Xenograft models
- Rodent tumor models for primary tumor and metastatic growth
- 2D and 3D cell culture
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
- Preclinical assessment of therapeutic efficacy in cell culture models and in ex vivo human tissue models
- Dietary / therapeutic intervention in long-term rodent models
- Mechanisms of action with small molecule inhibitors and Mabs
- Models for carcinogenesis and anti-carcinogenesis
- Biomarker detection and modulation
